As we celebrate Earth Day 2025, it’s important to remember that the spirit of Earth Day isn’t confined to just one day each year. Every day can — and should — be Earth Day. The choices we make, the actions we take, and the technologies we support all contribute to the long-term health of our planet. In fact, the small, consistent steps we take every day are just as important as those big moments of awareness and action.
This year, the theme of Earth Day is “Our Power, Our Planet”, but the truth is, we don’t have to wait a year to make a difference. Whether it’s in our personal lives, within our communities, or in the industries that drive our economies, sustainability is a daily responsibility, and one we all have the power to take on. One industry in particular that drives sustainability forward in our consumerist world is the additive manufacturing industry.
Why Every Day Matters: Sustainability as a Constant Commitment
Traditional manufacturing often involves cutting, drilling, and shaping raw materials, resulting in significant waste. In fact, according to Business Waste, approximately 9.2 billion tons of industrial waste are generated worldwide every year. (Yes, billion!) However, unlike typical manufacturing, 3D printing is an additive process, meaning that it builds objects layer by layer, using only the material necessary for the product. This method helps manufacturers eliminate overproduction and greatly reduce the environmental impact of their production. This means that every single print job made through additive manufacturing is an intentional step toward reducing material waste, making it a sustainable choice every day.
The process of 3D printing also directly contributes to energy conservation. Unlike traditional manufacturing, which relies on massive factories and energy-intensive machinery, 3D printing operates with significantly less energy consumption. The printer uses only the energy needed to create the object, making it more efficient and reducing the strain on energy resources. For context, traditional manufacturing uses an estimated 18.2 billion gallons of water per day. This reduction in energy consumption happens daily, meaning that every day, additive manufacturing helps lower our collective environmental footprint.
Localized Production: Reducing Carbon Emissions Every Day
In traditional manufacturing, products often travel long distances from factories to consumers, contributing to a significant amount of carbon emissions. This is especially true for global supply chains, where goods are shipped across countries and continents. Additive manufacturing, however, allows for localized production, meaning products can be made closer to their final destination, often on-demand.

By producing items near their point of use, 3D printing reduces the need for long-distance shipping, cutting down on transportation-related emissions. This reduction in carbon footprint is a daily contribution to sustainability. When products are made locally, they can be produced without the large, wasteful transportation footprint associated with traditional manufacturing, which makes every print job a small but impactful action toward a greener future.
Recycling and Repurposing: A Closed-Loop System for Sustainability
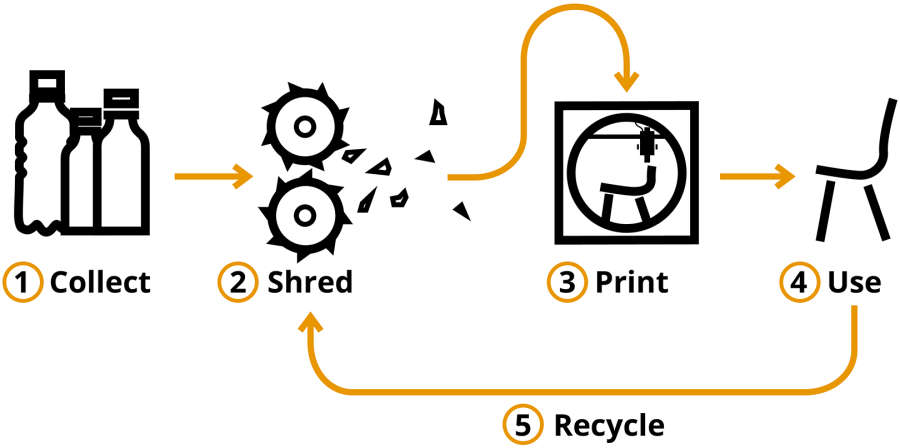
One of the most exciting features of additive manufacturing is its ability to recycle and repurpose materials. In traditional manufacturing, errors and excess materials often go to waste. However, with 3D printing, mistakes or leftover materials can be recycled and reused for future prints, keeping resources in circulation and reducing waste. This ongoing, closed-loop system ensures that materials are used efficiently and reduces the demand for new resources.
At ABCorp 3D, for example, we use sustainable materials like PA11, a nylon derived from vegetable castor oil, which has a 70% recycled content. We also use PA12, with an 80% recycling rate. By recycling unused materials back into the production process, we’re reducing waste every time we print a part. This is a perfect example of how 3D printing is not just a green solution on Earth Day, but a daily practice that reduces material consumption and contributes to a circular economy.
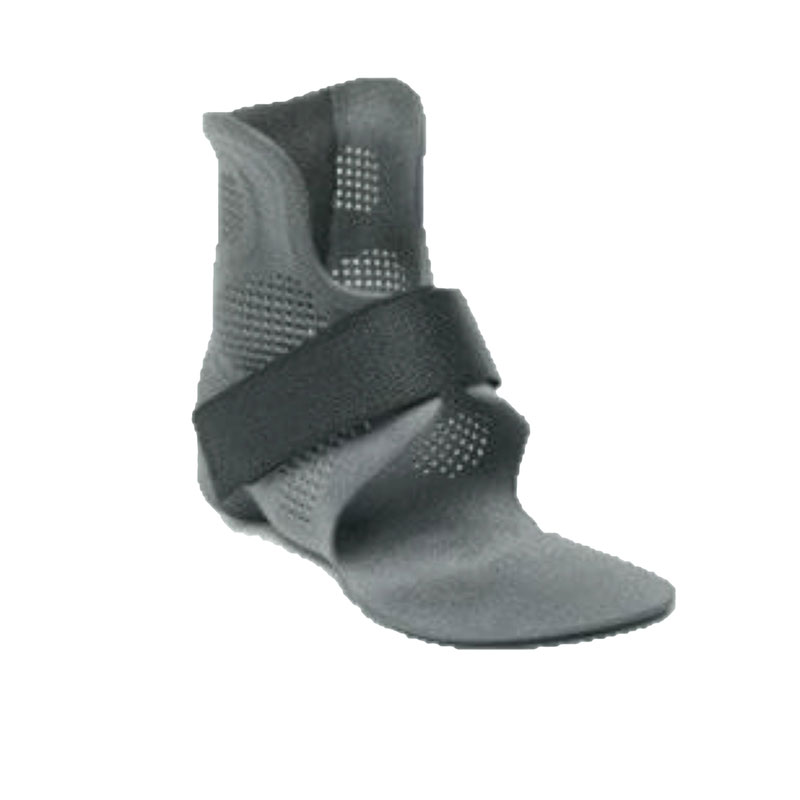 Everyday Innovation in Healthcare: Sustainable Solutions for Life
Everyday Innovation in Healthcare: Sustainable Solutions for Life
Sustainability isn’t limited to just consumer products. Additive manufacturing is also transforming the healthcare industry by enabling the production of custom medical devices like prosthetics and implants. These products can be made on-demand and tailored to individual patients, reducing the need for mass production and minimizing waste.
At ABCorp 3D, we create FDA-approved prosthetics and medical devices using 3D printing. By leveraging this technology, we not only provide personalized solutions but also contribute to a more sustainable healthcare system. The ability to produce these items on-demand, without the need for excessive inventory or large manufacturing facilities, means that healthcare is benefiting from the environmental advantages of additive manufacturing every day. Through 3D printing, the healthcare industry is becoming more sustainable, ensuring that patients get the care they need while minimizing environmental impact.
The Bigger Picture: How Additive Manufacturing Supports a Greener Future
Every time a product is made using 3D printing, we’re taking another step toward a more sustainable future. From reducing waste and energy use to enabling localized production and creating closed-loop recycling systems, additive manufacturing is making a measurable difference. It’s not just a technology for Earth Day; it’s a technology that makes sustainability possible every single day.
By embracing additive manufacturing, industries can streamline their processes, reduce their carbon footprints, and contribute to a more sustainable future. Whether it’s making consumer goods, medical devices, or industrial parts, 3D printing offers an ongoing solution to the challenges of resource depletion and environmental impact. And because it’s an evolving and adaptive technology, its potential to drive sustainability will only continue to grow.
As we celebrate Earth Day 2025, let’s remember that sustainability isn’t a one-time event; it’s a daily commitment, and additive manufacturing is helping industries and businesses like ABCorp make that commitment easier by enabling greener, more efficient production. We hope you will join us in supporting and embracing technologies like 3D printing that allow us to make every day Earth Day.